The Ultimate Guide to Sail Types and Rigs (with Pictures)
What's that sail for? Generally, I don't know. So I've come up with a system. I'll explain you everything there is to know about sails and rigs in this article.
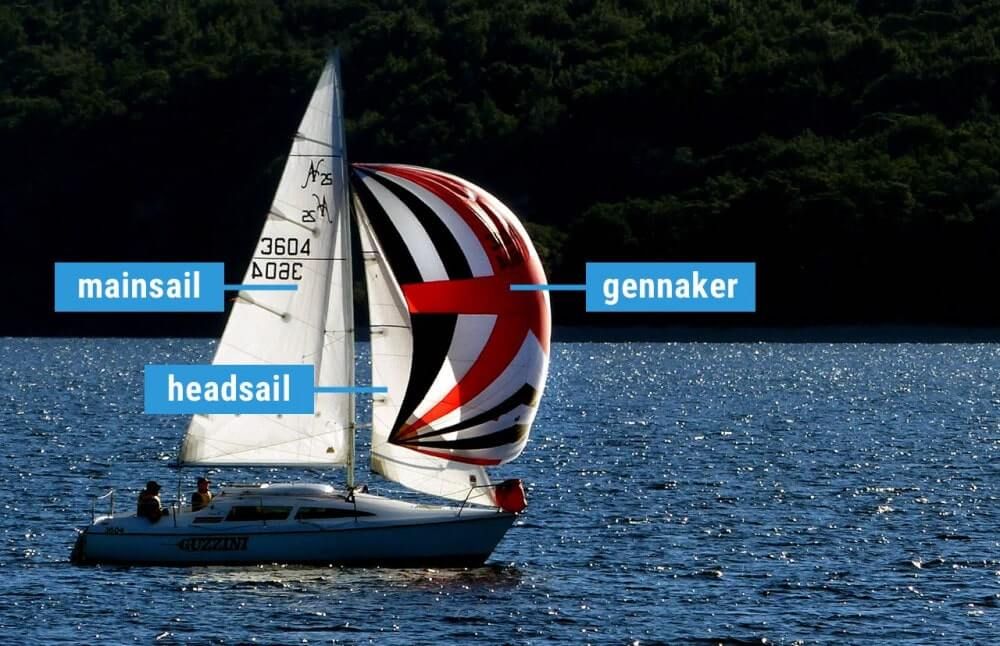
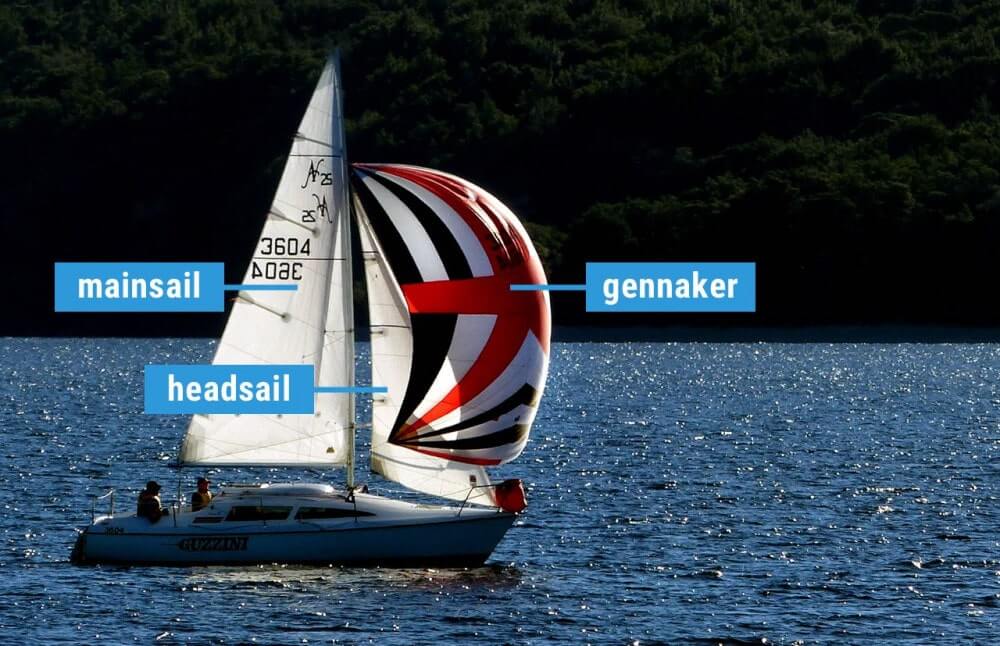
What are the different types of sails? Most sailboats have one mainsail and one headsail. Typically, the mainsail is a fore-and-aft bermuda rig (triangular shaped). A jib or genoa is used for the headsail. Most sailors use additional sails for different conditions: the spinnaker (a common downwind sail), gennaker, code zero (for upwind use), and stormsail.
Each sail has its own use. Want to go downwind fast? Use a spinnaker. But you can't just raise any sail and go for it. It's important to understand when (and how) to use each sail. Your rigging also impacts what sails you can use.

On this page:
This article is part 1 of my series on sails and rig types. Part 2 is all about the different types of rigging. If you want to learn to identify every boat you see quickly, make sure to read it. It really explains the different sail plans and types of rigging clearly.

Guide to Understanding Sail Rig Types (with Pictures)
Different Sail Types
First I'll give you a quick and dirty overview of sails in this list below. Then, I'll walk you through the details of each sail type, and the sail plan, which is the godfather of sail type selection so to speak.
Click here if you just want to scroll through a bunch of pictures.
Here's a list of different models of sails:
(Don't worry if you don't yet understand some of the words, I'll explain all of them in a bit)
- Mainsail
- Jib - triangular staysail
- Genoa - large jib that overlaps the mainsail
- Spinnaker - large balloon-shaped downwind sail for light airs
- Gennaker - crossover between a Genoa and Spinnaker
- Code Zero or Screecher - upwind spinnaker
- Drifter or reacher - a large, powerful, hanked on genoa, but made from lightweight fabric
- Windseeker - tall, narrow, high-clewed, and lightweight jib
- Trysail - smaller front-and-aft mainsail for heavy weather
- Storm jib - small jib for heavy weather
I have a big table below that explains the sail types and uses in detail.
I know, I know ... this list is kind of messy, so to understand each sail, let's place them in a system.
The first important distinction between sail types is the placement. The mainsail is placed aft of the mast, which simply means behind. The headsail is in front of the mast.
Generally, we have three sorts of sails on our boat:
- Mainsail: The large sail behind the mast which is attached to the mast and boom
- Headsail: The small sail in front of the mast, attached to the mast and forestay (ie. jib or genoa)
- Specialty sails: Any special utility sails, like spinnakers - large, balloon-shaped sails for downwind use
The second important distinction we need to make is the functionality. Specialty sails (just a name I came up with) each have different functionalities and are used for very specific conditions. So they're not always up, but most sailors carry one or more of these sails.
They are mostly attached in front of the headsail, or used as a headsail replacement.
The specialty sails can be divided into three different categories:
- downwind sails - like a spinnaker
- light air or reacher sails - like a code zero
- storm sails

The parts of any sail
Whether large or small, each sail consists roughly of the same elements. For clarity's sake I've took an image of a sail from the world wide webs and added the different part names to it:

- Head: Top of the sail
- Tack: Lower front corner of the sail
- Foot: Bottom of the sail
- Luff: Forward edge of the sail
- Leech: Back edge of the sail
- Clew: Bottom back corner of the sail
So now we speak the same language, let's dive into the real nitty gritty.
Basic sail shapes
Roughly speaking, there are actually just two sail shapes, so that's easy enough. You get to choose from:
- square rigged sails
- fore-and-aft rigged sails
I would definitely recommend fore-and-aft rigged sails. Square shaped sails are pretty outdated. The fore-and-aft rig offers unbeatable maneuverability, so that's what most sailing yachts use nowadays.

Square sails were used on Viking longships and are good at sailing downwind. They run from side to side. However, they're pretty useless upwind.
A fore-and-aft sail runs from the front of the mast to the stern. Fore-and-aft literally means 'in front and behind'. Boats with fore-and-aft rigged sails are better at sailing upwind and maneuvering in general. This type of sail was first used on Arabic boats.
The Sail Plan of a Bermuda Sloop
As a beginner sailor I confuse the type of sail with rigging all the time. But I should cut myself some slack, because the rigging and sails on a boat are very closely related. They are all part of the sail plan.
A sail plan is made up of:
- Mast configuration - refers to the number of masts and where they are placed
- Sail type - refers to the sail shape and functionality
- Rig type - refers to the way these sails are set up on your boat
There are dozens of sails and hundreds of possible configurations (or sail plans).
For example, depending on your mast configuration, you can have extra headsails (which then are called staysails).
The shape of the sails depends on the rigging, so they overlap a bit. To keep it simple I'll first go over the different sail types based on the most common rig. I'll go over the other rig types later in the article.
Bermuda Sloop: the most common rig
Most modern small and mid-sized sailboats have a Bermuda sloop configuration. The sloop is one-masted and has two sails, which are front-and-aft rigged. This type of rig is also called a Marconi Rig. The Bermuda rig uses a triangular sail, with just one side of the sail attached to the mast.
The mainsail is in use most of the time. It can be reefed down, making it smaller depending on the wind conditions. It can be reefed down completely, which is more common in heavy weather. (If you didn't know already: reefing is skipper terms for rolling or folding down a sail.)
In very strong winds (above 30 knots), most sailors only use the headsail or switch to a trysail.

The headsail powers your bow, the mainsail powers your stern (rear). By having two sails, you can steer by using only your sails (in theory - it requires experience). In any case, two sails gives you better handling than one, but is still easy to operate.
Mainsail Designs
Let's get to the actual sails. The mainsail is attached behind the mast and to the boom, running to the stern. There are multiple designs, but they actually don't differ that much. So the following list is a bit boring. Feel free to skip it or quickly glance over it.
- Square Top racing mainsail - has a high performance profile thanks to the square top, optional reef points
- Racing mainsail - made for speed, optional reef points
- Cruising mainsail - low-maintenance, easy to use, made to last. Generally have one or multiple reef points.
- Full-Batten Cruising mainsail - cruising mainsail with better shape control. Eliminates flogging. Full-length battens means the sail is reinforced over the entire length. Generally have one or multiple reef points.
- High Roach mainsail - crossover between square top racing and cruising mainsail, used mostly on cats and multihulls. Generally have one or multiple reef points.
- Mast Furling mainsail - sails specially made to roll up inside the mast - very convenient but less control; of sail shape. Have no reef points
- Boom Furling mainsail - sails specially made to roll up inside the boom. Have no reef points.
Headsail Options
The headsail is the front sail in a front-and-aft rig. The sail is fixed on a stay (rope, wire or rod) which runs forward to the deck or bowsprit. It's almost always triangular (Dutch fishermen are known to use rectangular headsail). A triangular headsail is also called a jib.
Headsails can be attached in two ways:
- using roller furlings - the sail rolls around the headstay
- hank on - fixed attachment
Types of jibs:
Typically a sloop carries a regular jib as its headsail. It can also use a genoa.
- A jib is a triangular staysail set in front of the mast. It's the same size as the fore-triangle.
- A genoa is a large jib that overlaps the mainsail.
Jib
What's the purpose of a jib sail? A jib is used to improve handling and to increase sail area on a sailboat. This helps to increase speed. The jib gives control over the bow (front) of the ship, making it easier to maneuver the ship. The mainsail gives control over the stern of the ship. The jib is the headsail (frontsail) on a front-and-aft rig.
The size of the jib is generally indicated by a number - J1, 2, 3, and so on. The number tells us the attachment point. The order of attachment points may differ per sailmaker, so sometimes J1 is the largest jib (on the longest stay) and sometimes it's the smallest (on the shortest stay). Typically the J1 jib is the largest - and the J3 jib the smallest.
Most jibs are roller furling jibs: this means they are attached to a stay and can be reefed down single-handedly. If you have a roller furling you can reef down the jib to all three positions and don't need to carry different sizes.
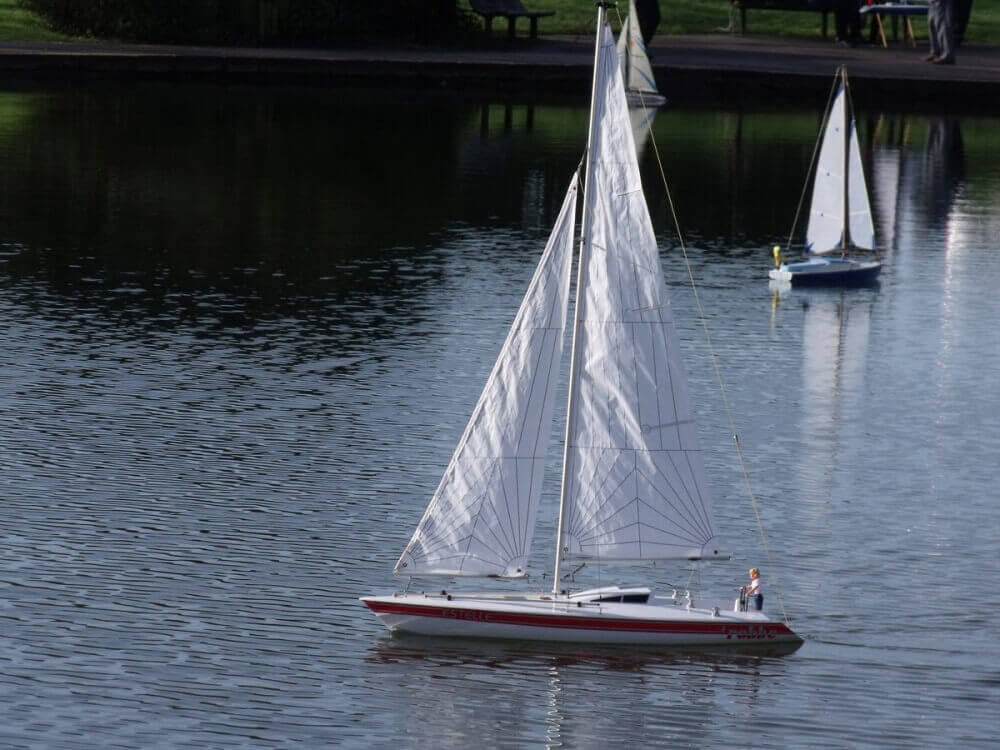

Genoa
Originally called the 'overlapping jib', the leech of the genoa extends aft of the mast. This increases speed in light and moderate winds. A genoa is larger than the total size of the fore-triangle. How large exactly is indicated by a percentage.
- A number 1 genoa is typically 155% (it used to be 180%)
- A number 2 genoa is typically 125-140%
Genoas are typically made from 1.5US/oz polyester spinnaker cloth, or very light laminate.
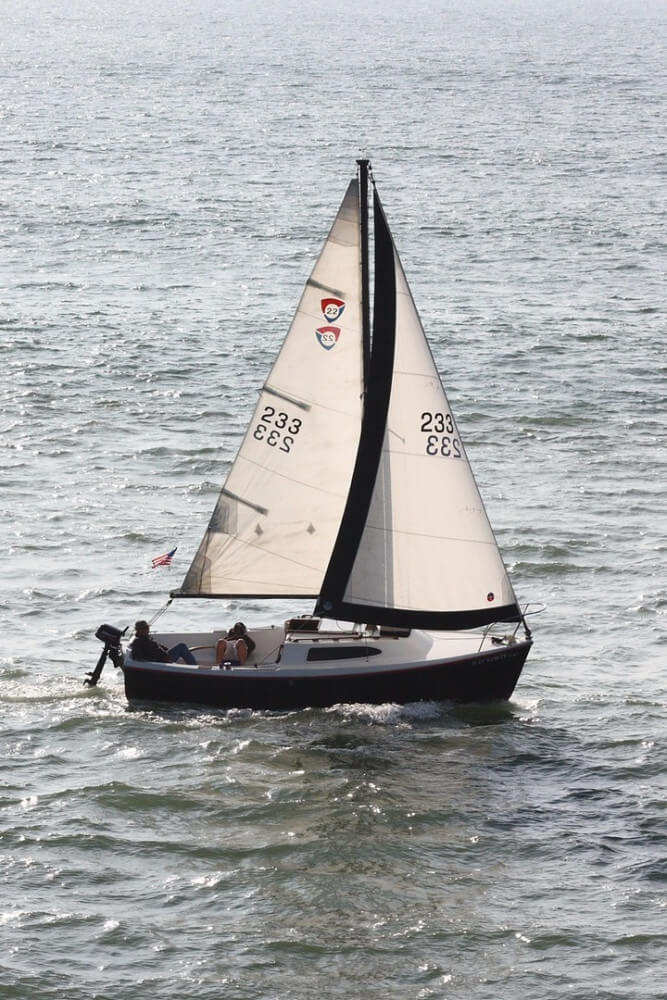

Specialty Sails
This is where it gets pretty interesting. You can use all kinds of sails to increase speed, handling, and performance for different weather conditions.
Some rules of thumb:
- Large sails are typically good for downwind use, small sails are good for upwind use.
- Large sails are good for weak winds (light air), small sails are good for strong winds (storms).
Downwind sails
Thanks to the front-and-aft rig sailboats are easier to maneuver, but they catch less wind as well. Downwind sails are used to offset this by using a large sail surface, pulling a sailboat downwind. They can be hanked on when needed and are typically balloon shaped.
Here are the most common downwind sails:
- Spinnaker
- Big gennaker
- Small gennaker
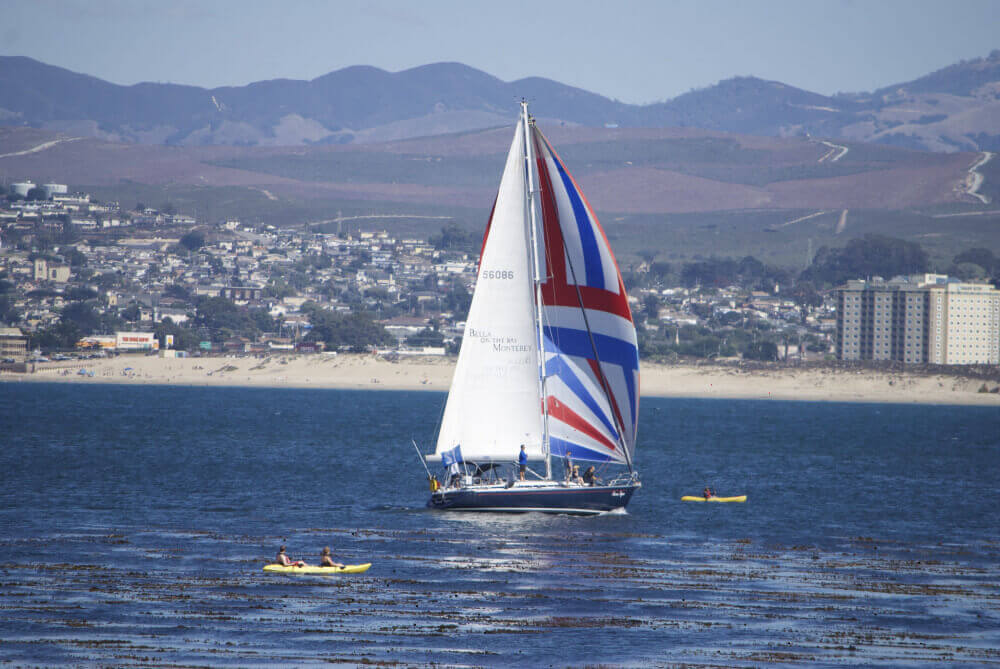
Spinnaker
A free-flying sail that fills up with air, giving it a balloon shape. Spinnakers are generally colorful, which is why they look like kites. This downwind sail has the largest sail area, and it's capable of moving a boat with very light wind. They are amazing to use on trade wind routes, where they can help you make quick progress.
Spinnakers require special rigging. You need a special pole and track on your mast. You attach the sail at three points: in the mast head using a halyard, on a pole, and on a sheet.
The spinnaker is symmetrical, meaning the luff is as long as its leech. It's designed for broad reaching.

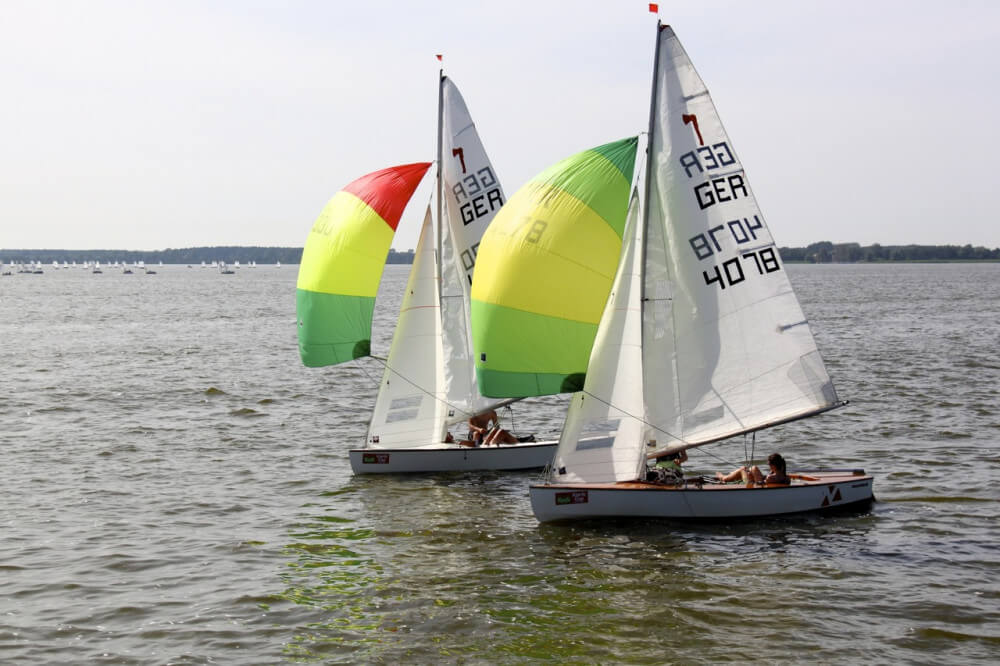
Gennaker or cruising spinnaker
The Gennaker is a cross between the genoa and the spinnaker. It has less downwind performance than the spinnaker. It is a bit smaller, making it slower, but also easier to handle - while it remains very capable. The cruising spinnaker is designed for broad reaching.
The gennaker is a smaller, asymmetric spinnaker that's doesn't require a pole or track on the mast. Like the spinnaker, and unlike the genoa, the gennaker is set flying. Asymmetric means its luff is longer than its leech.
You can get big and small gennakers (roughly 75% and 50% the size of a true spinnaker).
Also called ...
- the cruising spinnaker
- cruising chute
- pole-less spinnaker
- SpinDrifter
... it's all the same sail.

Light air sails
There's a bit of overlap between the downwind sails and light air sails. Downwind sails can be used as light air sails, but not all light air sails can be used downwind.
Here are the most common light air sails:
- Spinnaker and gennaker
- Drifter reacher
- Code zero reacher
- Windseeker
Drifter reacher
A drifter (also called a reacher) is a lightweight, larger genoa for use in light winds. It's roughly 150-170% the size of a genoa. It's made from very lightweight laminated spinnaker fabric (1.5US/oz).
Thanks to the extra sail area the sail offers better downwind performance than a genoa. It's generally made from lightweight nylon. Thanks to it's genoa characteristics the sail is easier to use than a cruising spinnaker.
Code zero reacher
The code zero reacher is officially a type of spinnaker, but it looks a lot like a large genoa. And that's exactly what it is: a hybrid cross between the genoa and the asymmetrical spinnaker (gennaker). The code zero however is designed for close reaching, making it much flatter than the spinnaker. It's about twice the size of a non-overlapping jib.

Windseeker
A windseeker is a small, free-flying staysail for super light air. It's tall and thin. It's freestanding, so it's not attached to the headstay. The tack attaches to a deck pad-eye. Use your spinnakers' halyard to raise it and tension the luff.
It's made from nylon or polyester spinnaker cloth (0.75 to 1.5US/oz).
It's designed to guide light air onto the lee side of the main sail, ensuring a more even, smooth flow of air.
Stormsails
Stormsails are stronger than regular sails, and are designed to handle winds of over 45 knots. You carry them to spare the mainsail. Sails
A storm jib is a small triangular staysail for use in heavy weather. If you participate in offshore racing you need a mandatory orange storm jib. It's part of ISAF's requirements.
A trysail is a storm replacement for the mainsail. It's small, triangular, and it uses a permanently attached pennant. This allows it to be set above the gooseneck. It's recommended to have a separate track on your mast for it - you don't want to fiddle around when you actually really need it to be raised ... now.

Complete Overview of Sail Uses
| Sail | Type | Shape | Wind speed | Size | Wind angle |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bermuda | mainsail | triangular, high sail | < 30 kts | ||
| Jib | headsail | small triangular foresail | < 45 kts | 100% of foretriangle | |
| Genoa | headsail | jib that overlaps mainsail | < 30 kts | 125-155% of foretriangle | |
| Spinnaker | downwind | free-flying, balloon shape | 1-15 kts | 200% or more of mainsail | 90°–180° |
| Gennaker | downwind | free-flying, balloon shape | 1-20 kts | 85% of spinnaker | 75°-165° |
| Code Zero or screecher | light air & upwind | tight luffed, upwind spinnaker | 1-16 kts | 70-75% of spinnaker | |
| Storm Trysail | mainsail | small triangular mainsail replacement | > 45 kts | 17.5% of mainsail | |
| Drifter reacher | light air | large, light-weight genoa | 1-15 kts | 150-170% of genoa | 30°-90° |
| Windseeker | light air | free-flying staysail | 0-6 kts | 85-100% of foretriangle | |
| Storm jib | strong wind headsail | low triangular staysail | > 45 kts | < 65% height foretriangle |
Why Use Different Sails At All?
You could just get the largest furling genoa and use it on all positions. So why would you actually use different types of sails?
The main answer to that is efficiency. Some situations require other characteristics.
Having a deeply reefed genoa isn't as efficient as having a small J3. The reef creates too much draft in the sail, which increases heeling. A reefed down mainsail in strong winds also increases heeling. So having dedicated (storm) sails is probably a good thing, especially if you're planning more demanding passages or crossings.
But it's not just strong winds, but also light winds that can cause problems. Heavy sails will just flap around like laundry in very light air. So you need more lightweight fabrics to get you moving.
What Are Sails Made Of?
The most used materials for sails nowadays are:
- Dacron - woven polyester
- woven nylon
- laminated fabrics - increasingly popular
Sails used to be made of linen. As you can imagine, this is terrible material on open seas. Sails were rotting due to UV and saltwater. In the 19th century linen was replaced by cotton.
It was only in the 20th century that sails were made from synthetic fibers, which were much stronger and durable. Up until the 1980s most sails were made from Dacron. Nowadays, laminates using yellow aramids, Black Technora, carbon fiber and Spectra yarns are more and more used.
Laminates are as strong as Dacron, but a lot lighter - which matters with sails weighing up to 100 kg (220 pounds).
By the way: we think that Viking sails were made from wool and leather, which is quite impressive if you ask me.
Mast Configurations and Rig Types
In this section of the article I give you a quick and dirty summary of different sail plans or rig types which will help you to identify boats quickly. But if you want to really understand it clearly, I really recommend you read part 2 of this series, which is all about different rig types.
You can't simply count the number of masts to identify rig type
But you can identify any rig type if you know what to look for. We've created an entire system for recognizing rig types. Let us walk you through it.
Read all about sail rig types
As I've said earlier, there are two major rig types: square rigged and fore-and-aft. We can divide the fore-and-aft rigs into three groups:
- Bermuda rig (we have talked about this one the whole time) - has a three-sided mainsail
- Gaff rig - has a four-sided mainsail, the head of the mainsail is guided by a gaff
- Lateen rig - has a three-sided mainsail on a long yard
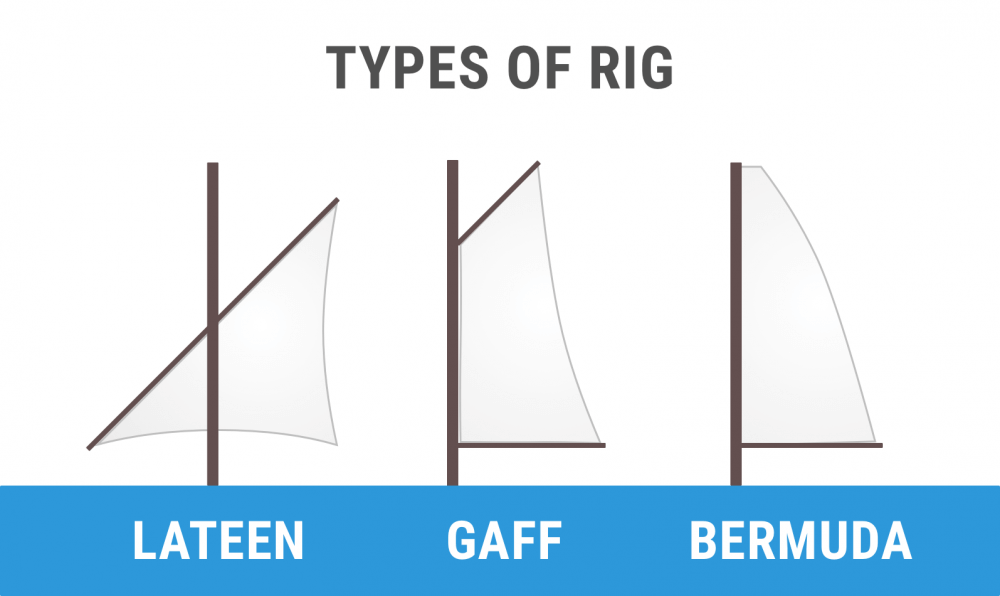
There are roughly four types of boats:
- one masted boats - sloop, cutter
- two masted boats - ketch, schooner, brig
- three masted - barque
- fully rigged or ship rigged - tall ship
Everything with four masts is called a (tall) ship. I think it's outside the scope of this article, but I have written a comprehensive guide to rigging. I'll leave the three and four-masted rigs for now. If you want to know more, I encourage you to read part 2 of this series.
One-masted rigs
Boats with one mast can have either one sail, two sails, or three or more sails.
The 3 most common one-masted rigs are:
- Cat - one mast, one sail
- Sloop - one mast, two sails
- Cutter - one mast, three or more sails
1. Gaff Cat
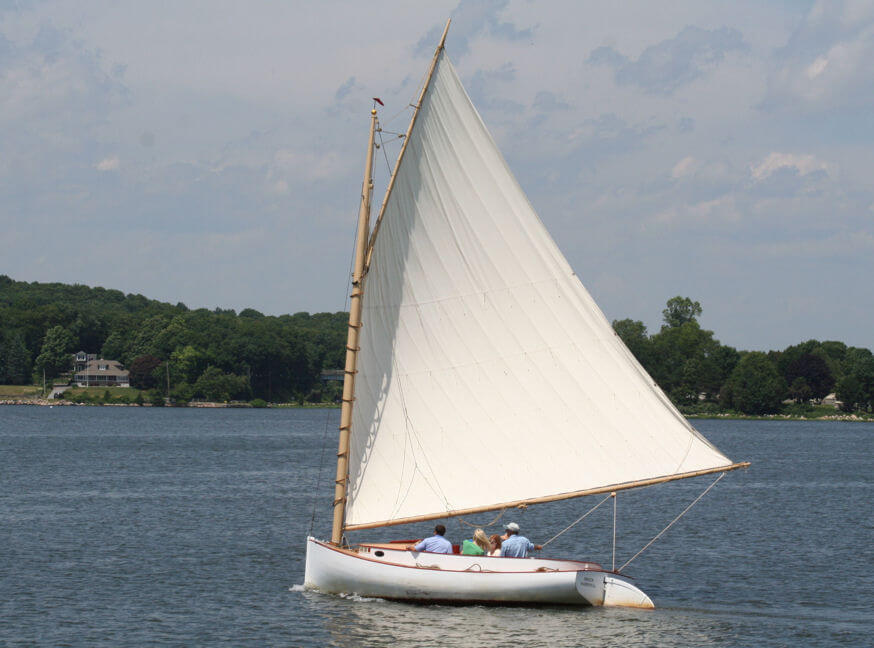

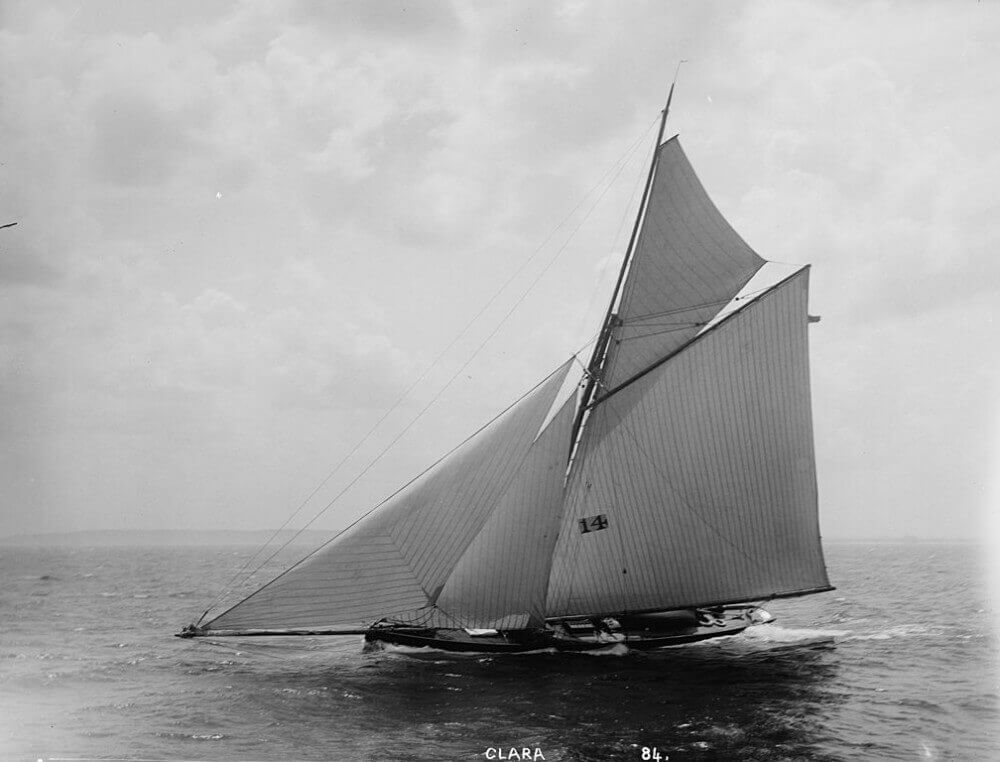
2. Gaff Sloop
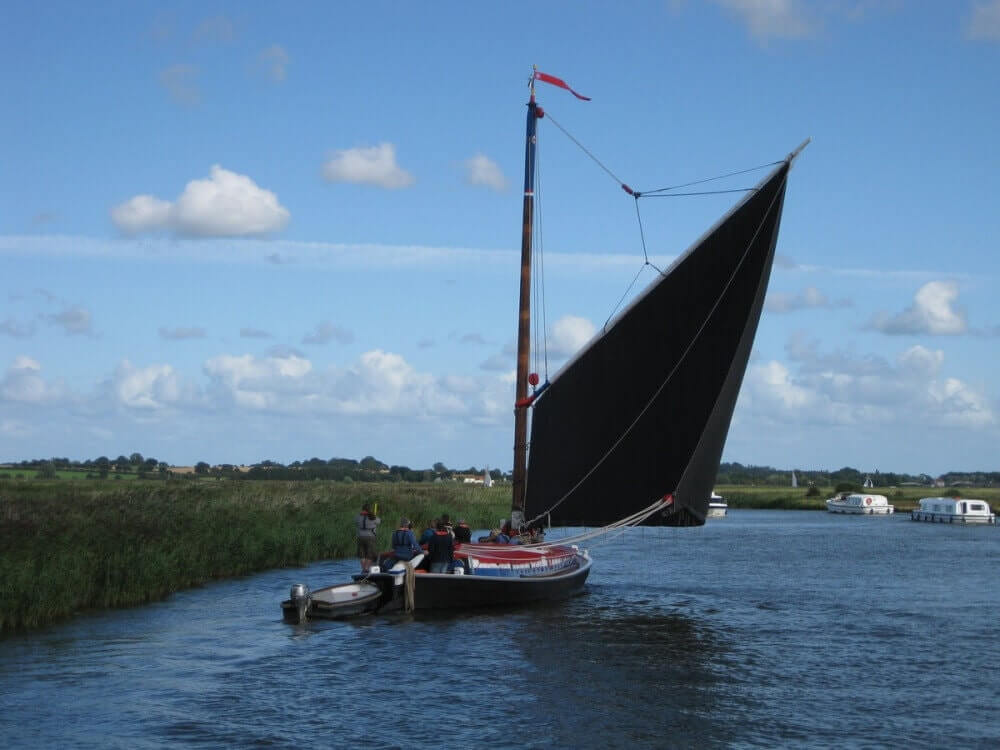

3. Cutter

Two-masted rigs
Two-masted boats can have an extra mast in front or behind the main mast. Behind (aft of) the main mast is called a mizzen mast. In front of the main mast is called a foremast.
The 5 most common two-masted rigs are:
- Lugger - two masts (mizzen), with lugsail (cross between gaff rig and lateen rig) on both masts
- Yawl - two masts (mizzen), fore-and-aft rigged on both masts. Main mast much taller than mizzen. Mizzen without mainsail.
- Ketch - two masts (mizzen), fore-and-aft rigged on both masts. Main mast with only slightly smaller mizzen. Mizzen has mainsail.
- Schooner - two masts (foremast), generally gaff rig on both masts. Main mast with only slightly smaller foremast. Sometimes build with three masts, up to seven in the age of sail.
- Brig - two masts (foremast), partially square-rigged. Main mast carries small lateen rigged sail.
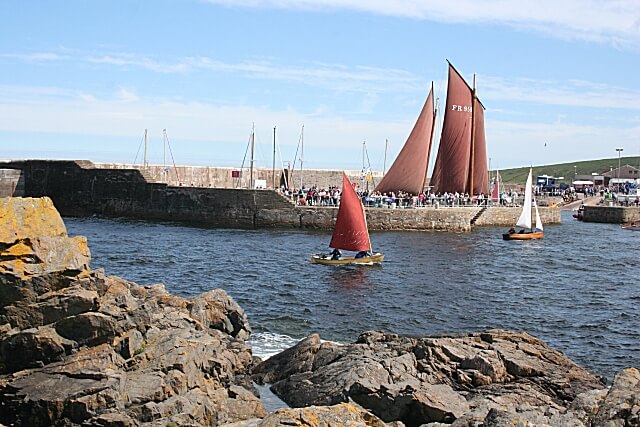
1. Lugger

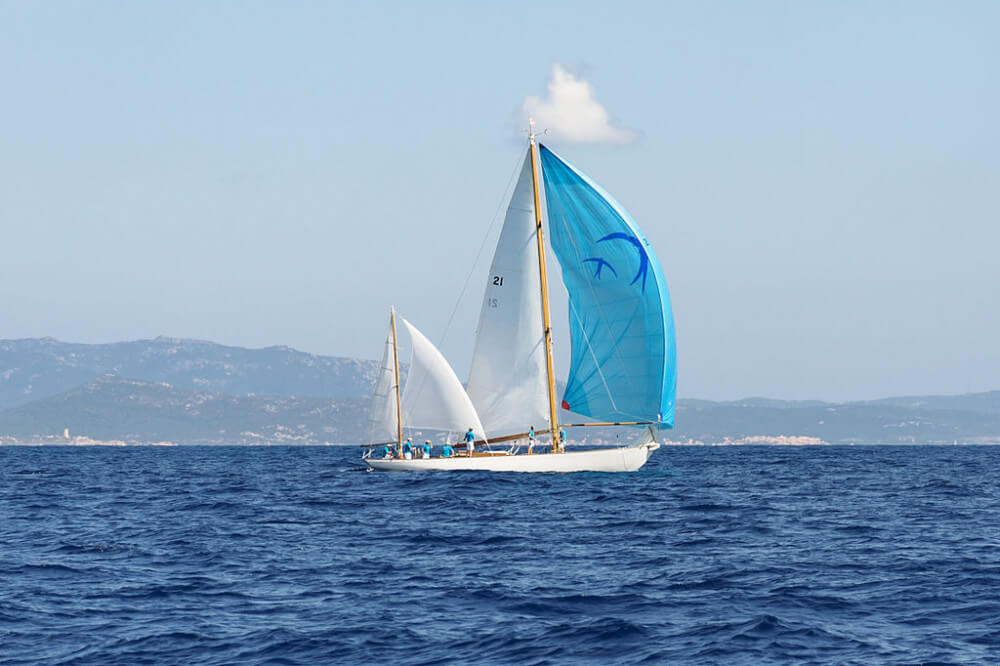
2. Yawl

3. Ketch
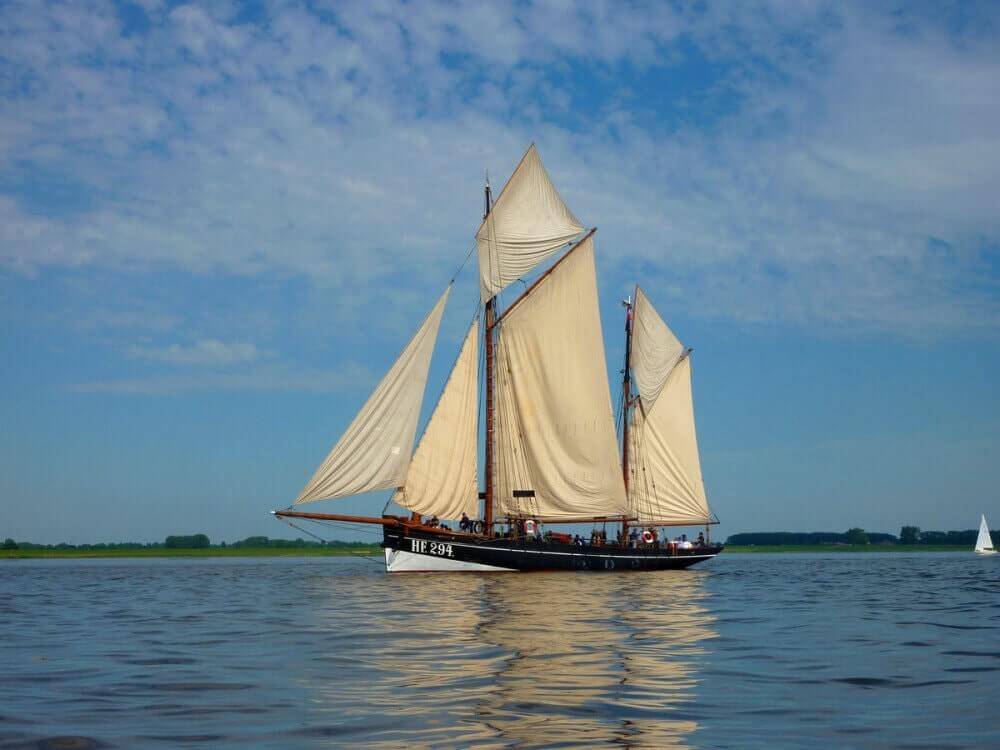

4. Schooner
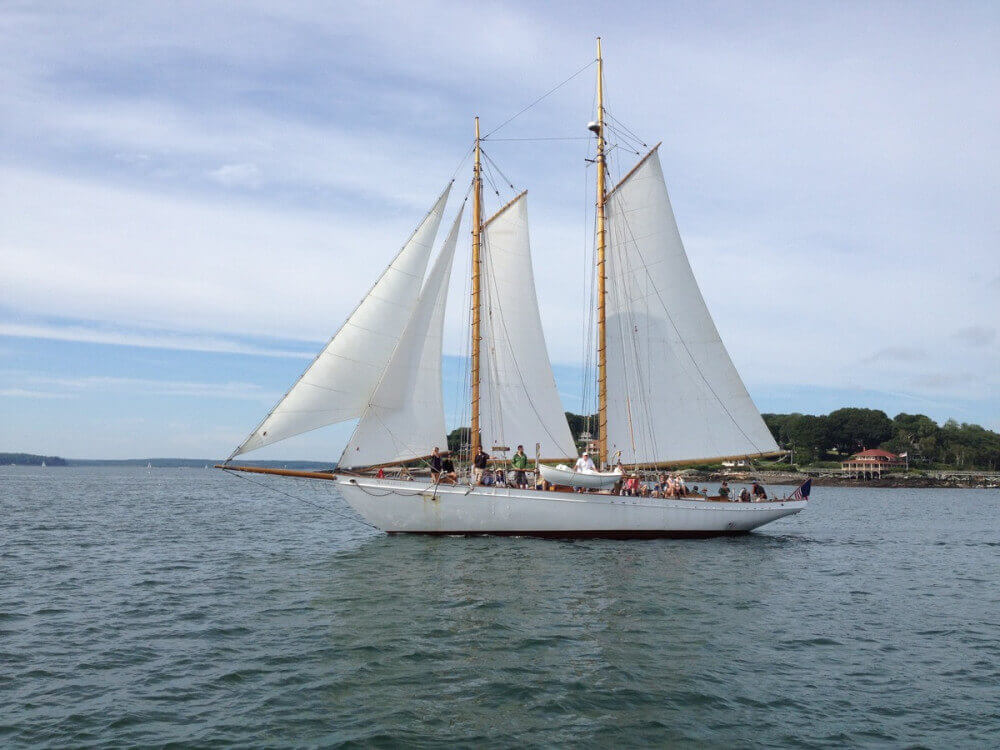

5. Brigantine

This article is part 1 of a series about sails and rig types
If you want to read on and learn to identify any sail plans and rig type, we've found a series of questions that will help you do that quickly.
Read all about recognizing rig types
Related Questions
What is the difference between a gennaker & spinnaker? Typically, a gennaker is smaller than a spinnaker. Unlike a spinnaker, a gennaker isn't symmetric. It's asymmetric like a genoa. It is however rigged like a spinnaker; it's not attached to the forestay (like a jib or a genoa). It's a downwind sail, and a cross between the genoa and the spinnaker (hence the name).
What is a Yankee sail? A Yankee sail is a jib with a high-cut clew of about 3' above the boom. A higher-clewed jib is good for reaching and is better in high waves, preventing the waves crash into the jibs foot. Yankee jibs are mostly used on traditional sailboats.
How much does a sail weigh? Sails weigh anywhere between 4.5-155 lbs (2-70 kg). The reason is that weight goes up exponentially with size. Small boats carry smaller sails (100 sq. ft.) made from thinner cloth (3.5 oz). Large racing yachts can carry sails of up to 400 sq. ft., made from heavy fabric (14 oz), totaling at 155 lbs (70 kg).
What's the difference between a headsail and a staysail? The headsail is the most forward of the staysails. A boat can only have one headsail, but it can have multiple staysails. Every staysail is attached to a forward running stay. However, not every staysail is located at the bow. A stay can run from the mizzen mast to the main mast as well.
What is a mizzenmast? A mizzenmast is the mast aft of the main mast (behind; at the stern) in a two or three-masted sailing rig. The mizzenmast is shorter than the main mast. It may carry a mainsail, for example with a ketch or lugger. It sometimes doesn't carry a mainsail, for example with a yawl, allowing it to be much shorter.
Special thanks to the following people for letting me use their quality photos:
- Bill Abbott - True Spinnaker with pole - CC BY-SA 2.0
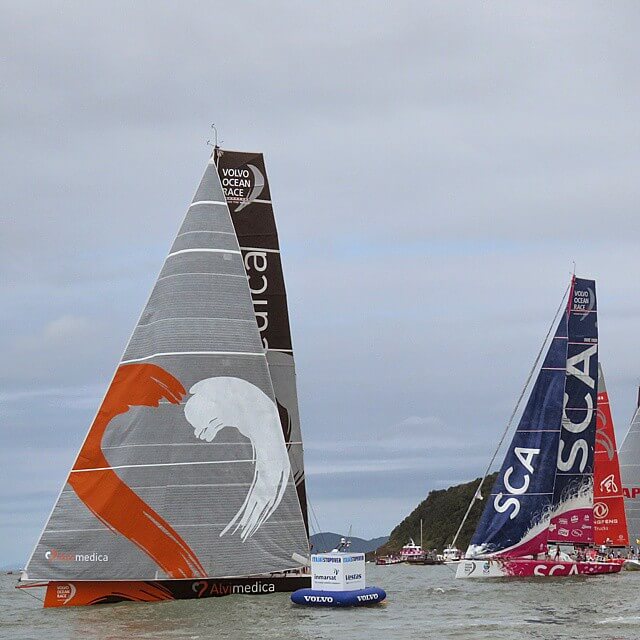
- lotsemann - Volvo Ocean Race Alvimedica and the Code Zero versus SCA and the J1 - CC BY-SA 2.0
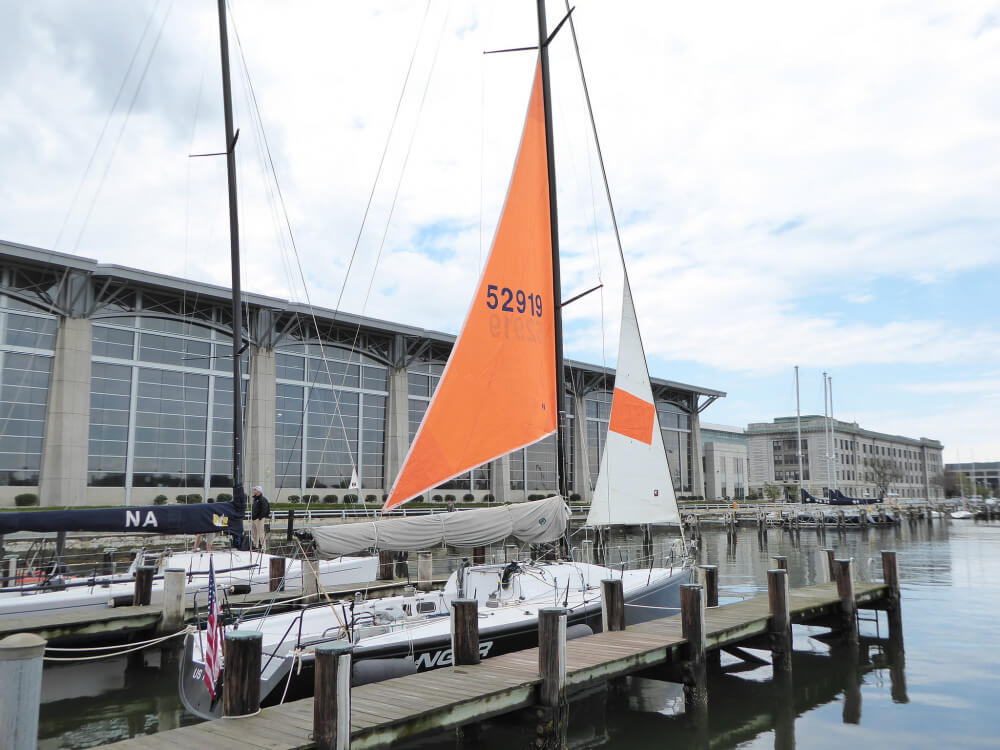
- Lisa Bat - US Naval Academy Trysail and Storm Jib dry fit - CC BY-SA 2.0
- Mike Powell - White gaff cat - CC BY-SA 2.0
- Anne Burgess - Lugger The Reaper at Scottish Traditional Boat Festival
Did you find the answer to your specific question?
👍 73 👎 20


Comments
Yannick
Hi, I stumbled upon your page and couldn’t help but notice some mistakes in your description of spinnakers and gennakers.
First of all, in the main photo on top of this page the small yacht is sailing a spinnaker, not a gennaker. If you look closely you can see the spinnaker pole standing on the mast, visible between the main and headsail. Further down, the discription of the picture with the two German dinghies is incorrect. They are sailing spinnakers, on a spinnaker pole. In the farthest boat, you can see a small piece of the pole.
If needed I can give you the details on the difference between gennakers and spinnakers correctly?
George
Hi Shawn,
I am living in Utrecht
I have an old gulf 32 and I am sailing in merkmeer
I find your articles very helpful
Thanks
Elmer
Thank you for helping me under stand all the sails there names and what there functions were and how to use them. I am planning to build a trimaran 30’ what would be the best sails to have I plan to be coastal sailing with it. Thank you
Gowtham
Hey Comrade!
Well done with your master piece blogging. Just a small feedback. “The jib gives control over the bow of the ship, making it easier to maneuver the ship. The mainsail gives control over the stern of the ship.” Can you please first tell the different part of a sail boat earlier and then talk about bow and stern later in the paragraph. A reader has no clue on the newly introduced terms. It helps to keep laser focused and not forget main concepts.
Thanks.
CvB
Shawn, I am currently reading How to sail around the World” by Hal Roth. Yes, I want to sail around the world. His book is truly grounded in real world experience but like a lot of very knowledgable people discussing their area of expertise, Hal uses a lot of terms that I probably should have known but didn’t, until now. I am now off to read your second article. Thank You for this very enlightening article on Sail types and their uses.
Shawn Buckles
HI CVB, that’s a cool plan. Thanks, I really love to hear that. I’m happy that it was helpful to you and I hope you are of to a great start for your new adventure!
Shawn Buckles
Hi GOWTHAM, thanks for the tip, I sometimes forget I haven’t specified the new term. I’ve added it to the article.
Yousif
Hello,
Nice article and video; however, you’re mixing up the spinnaker and the gennaker.
Vincent
A started out with a question. What distinguishes a brig from a schooner? Which in turn led to follow-up questions: I know there are Bermuda rigs and Latin rig, are there more? Which in turn led to further questions, and further, and further…
This site answers them all. Wonderful work. Thank you.
Raven Gray
Great post and video! One thing was I was surprised how little you mentioned the Ketch here and not at all in the video or chart, and your sample image is a large ship with many sails. Some may think Ketch’s are uncommon, old fashioned or only for large boats. Actually Ketch’s are quite common for cruisers and live-aboards, especially since they often result in a center cockpit layout which makes for a very nice aft stateroom inside. These are almost exclusively the boats we are looking at, so I was surprised you glossed over them.
Brian
Love the article and am finding it quite informative.
While I know it may seem obvious to 99% of your readers, I wish you had defined the terms “upwind” and “downwind.” I’m in the 1% that isn’t sure which one means “with the wind” (or in the direction the wind is blowing) and which one means “against the wind” (or opposite to the way the wind is blowing.)
paul adriaan kleimeer
like in all fields of syntax and terminology the terms are colouual meaning local and then spead as the technology spread so an history lesson gives a floral bouque its colour and in the case of notical terms span culture and history adds an detail that bring reverence to the study simply more memorable.
margaret
Hi,
I have a small yacht sail which was left in my lock-up over 30 years ago
I basically know nothing about sails and wondered if you could spread any light as to the make and use of said sail.
Someone said it was probably originally from a Wayfayer wooden yacht but wasn’t sure.
Any info would be must appreciated and indeed if would be of any use to your followers?
I can provide pics but don’t see how to include them at present
kind regards
John Behling
I own a small business, and I always appreciate candid feedback that gives me perspective on how I am doing and where I might improve. In that spirit, I am offering my impression of this web page. Do what you want with it.
I found your article, and as I read it sounded like just the information I was looking for. Unfortunately, there were so many advertisements interrupting the flow of the text that I just could not concentrate on the article. I understand the desire to monetize your work, and when you can do so, that is a great place to be, I am sure. But in my case at least, the experience was unpleasant. I ended up going back to my search, and selecting a different article to read. I don’t think I even got into the meat of the article, so I cannot comment on the article itself. I just thought you should know that you are at some degree chasing away readers and potential customers with the over-abundance of advertising on your page.
Leave a comment