5 Surprising Advantages of a Full Keel Sailboat
Modern keel designs favor fin keels, with the high-performance boats using bulbs with narrow chord sections and deep drafts. Very few full keel designs are being built today, but there is a huge secondary market of used boats with full keels. Many ocean sailors swear by them and love their full keeled boats. There are reasons they love them.
While fin and bulb keels outperform full keels in straight speed and performance, the full keel is not without benefits you can appreciate. Here are five distinct advantages of a full keel you may not know about.
- Full keels provide better tracking
- Full keels are integral to the hull construction
- Better rudder and propeller protection
- Full keels are more comfortable
- They have less draft than fin keels
There are a lot of great cruising boats with full keel designs. Before you let someone talk you out of that sweet beauty because of her keel, look at some things that you might like about that full-figured boat.

1. Full Keels Provide Better Tracking
A boat with a full keel keeps sailing in the direction you point it. That big keel is a little harder to turn, and while that can make backing into a slip a bit of trouble, it helps to set up balanced boat trim.
With correct sail trim on any boat, sailing can be a two finger affair and only need a light touch to keep the boat on the wind, on course and fast. Constant steering and adjustment of a boat's course slows you, as the rudder acts like a brake every time you turn it.
A full keel helps, because of the boat's inherent ability to keep going straight. Setting up the rig and sails to get the boat to track like it’s on rails is a lot easier, and many full-keeled boats will sail themselves in moderate conditions with proper trim. Fin and bulb keels keels are more likely to spin out a little and require more correction.
How does this help? At least three ways:
- Fewer touches on the wheel is more boat speed. Yes, a full keel boat is slower that a fin because of the drag caused by the large wetted surface area of the keel, but keeping the boat sailing in the groove is much easier when the boat wants to keep going where you pointed it.
- It's easier on autopilots and wind-vane steering. The less you work your autopilot the better. From saving wear and tear on the machinery to avoiding overloads and over steering, the stability of the full keel helps. And wind-vane steering is a natural fit for most full keel boats, as their inherent course stability makes this a smart pairing.
- Heaving to. Stopping your boat is an important capability, whether it's to get some sleep or a shower when shorthanded, to make a repair, or to ride out a storm. Most full-keeled boats heave to easily, whereas some fin and bulb keels struggle and take more practice and still don't stop as well.
2. Full Keels Are Integral to the Hull Construction
The keel and the boat are one. Well, not always one piece, but a full keel runs the length of the boat and is almost always integral to the hull construction. A grounding which rips a fin off a lighter boat may be just an inconvenience with a full keel.
Full keels run over 50% of the length of the hull and are often integral to the hull construction, with ballast inside the keel. External keels have a much smaller attachment surface and rely on high tensile keel bolts and toughened structures to suspend the keel from the hull.
Striking a rock or the bottom with a fin or bulb puts the shearing force from the collision on a smaller, more leveraged point on the hull, whereas a full keel disperses the force over most of the hull. While other keels are as strong and quite safe, the full keel is more resistant to these shearing and twisting forces because it spreads out the load.
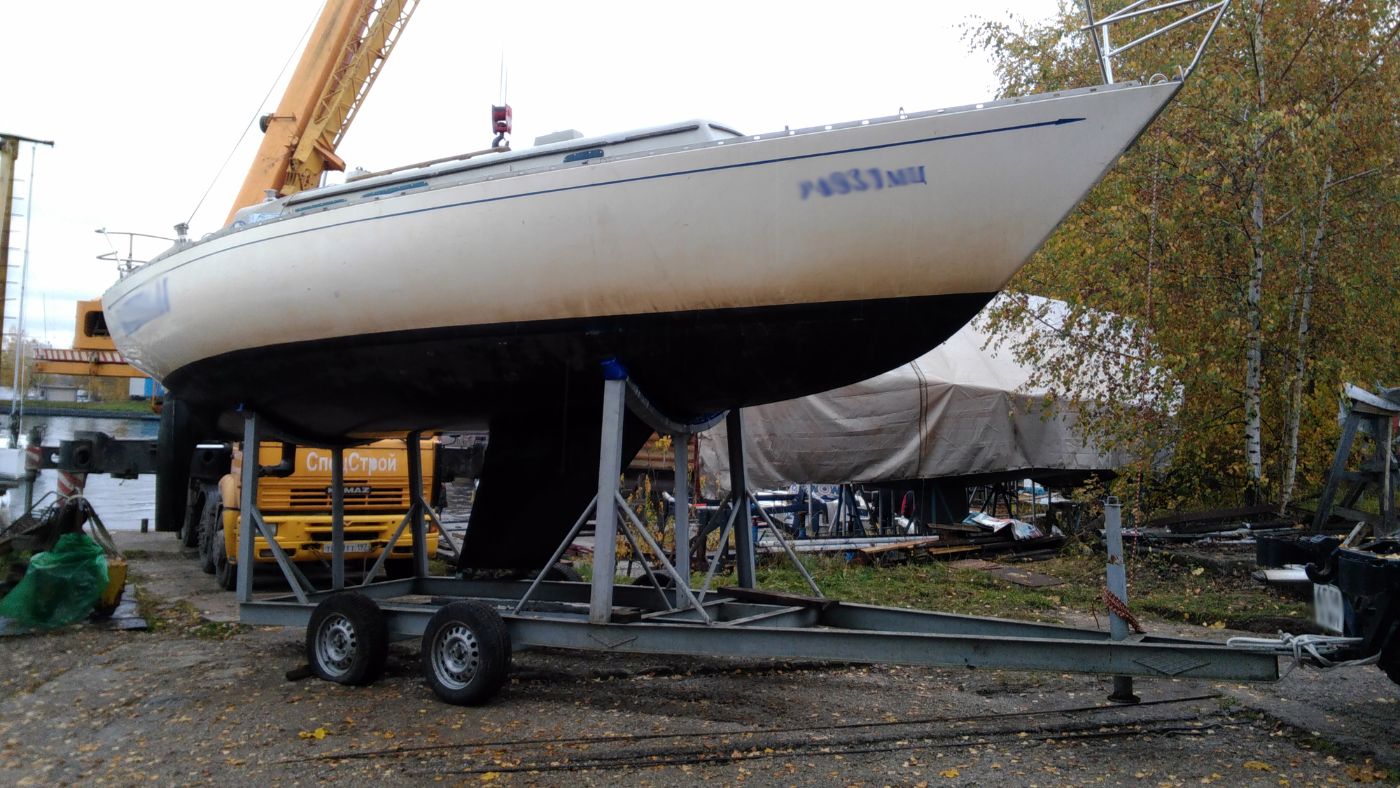

Grounded vessels with full keels will take less damage as the boat lies on its side waiting for the tide. Again it comes down to dispersing the load - putting the load of the grounded boat over a broader area reduces point loading and stress on any one component of the boat. Most full-keeled boats will just lie on their sides, waiting for the tide to come back in instead of tipping or rocking with swells and waves.
Also, grounding may be easier or softer with a full keel. Most full keels keep running on a slope matching the curve of the hull - the transition from hull to keel is gradual, not sudden. If you hit the bottom, you aren't hitting it at a ninety-degree angle with your boat, you're hitting a ramp. The sudden stop will be more of a slide up than a slam, and this equals better protection in a grounding.
3. Better Rudder & Propeller Protection
It's virtually impossible to catch your rudder on kelp or lobster pots when it's attached to the full trailing edge of the keel. And a propeller in an aperture is well protected from passing snags. If you're not motoring, it's very unlikely anything will get sucked into that space and wrapped on your prop.
It's not just protection from tangling and snags, either. Groundings can damage exposed spade and skeg rudders behind fin keels. Your full keel throws an enormous shadow for the more delicate parts of your underwater gear to hide behind, so they won't get damaged if you find the bottom.
4. Full Keels Are More Comfortable
Coupled with the tracking a full keel gives you is improved lateral stability - you roll less. While any ballast below water stops rolling by adding leverage and righting moment, the full keel uses more than just weight to slow your roll. The shape of the keel - a broad surface in the water - inherently resists rolling forces.
Righting Moment refers to a boat's tendency to come back up to upright when it's tipped or heeled. It's a combination of the movement of the center of buoyancy and the center of gravity of the boat as it tilts. More righting moment gives less heel angle.
Offshore, this gives you a better feel, more sea comfort. And sea comfort not only makes your passages easier, but in rough conditions is a safety feature. Lighter boats with fins and bulbs will get tossed and rolled in chop and waves, and that motion is exhausting. Not only do you have to constantly adjust your stance, grip and seating to handle the motion, sleeping, eating and cooking is that much more difficult.
Hours of sitting in the cockpit watching the autopilot in rough conditions can make your entire body feel you've been working out. You're always holding, bracing, and clenching something. A boat which makes the motions less violent and more natural will take that edge off. You won't have to hold and brace so much, and that keeps you from tiring as fast on watch.
The other place you'll love the stability is at anchor
The ideal anchorage is flat, calm and beautiful. But everyone likes that anchorage, and boat traffic and wakes aren't uncommon. Weather and wind shifts can make a calm anchorage uncomfortable as fetch carries over the water and makes chop. And sometimes, you just have to stay in an anchorage that just isn't that comfortable because it's the only one there is and it has chop or roll. (Academy Bay, I'm talking to you!)
That full keel stops a lot of roll and motion in the anchorage. Small fin-keeled boats thrash and roll violently when a big wake hits an anchorage, only the bigger, heavier boats are spared. But with a full keel you'll roll like a boat twice your size, spill a lot fewer drinks, and sleep better.
5. Less Draft as Other Designs (but As Stable)
The size of a full keel gives some stability; with added internal ballast you can get good stiffness and stability to the boat. Other keels don't have that same size and have to take alternative approaches to get the same stability.
A fin or bulb keel is a lever against the forces above the waterline from the rig and sails trying to tip the boat. You counteract those forces with weight - ballast. With a lever, you can increase the righting force two ways - add more weight, or make the lever longer.
A longer lever equals a deeper keel.
Deeper draft equates to better sail performance and righting moment, but you can get the needed stability on a full-keeled boat with less draft. Fin and bulb keels are deeper to get the extra righting forces they can't get from the longer, full keel.
Trends in modern keel design have led to deeper and deeper drafts, which close off some waters to some boats and make navigation trickier. Two or three feet of extra draft can close you out of a lot of anchorages and gunkholes.
Other Keel Designs to Consider
There are dozens of keel types out there and all serve a different purpose and excel under different conditions. To understand which keel type is best for your situation, I recommend you read our Illustrated Guide to Sailboat Keel Types, which contains the fundamentals of keel design and an overview for each keel type's characteristics (including diagrams). It will help you understand which keel designs to consider in ten minutes or less.
Did you find the answer to your specific question?
👍 32 👎 2




Leave a comment